Desert architecture
Described desert areas:
- Areas where humidity is less than 40%.
- Average annual temperature greater than 18 degrees Celsius.
- The average annual rainfall is less than 200 mm.
Desert areas are characterized by relatively harsh environmental conditions:
The temperature difference between day and night is high, the summer is hot and the winter is cold, there are extreme changes in relative humidity, solar radiation is very powerful, the absence of vegetation, the landscape with the monochrome colors all affect the person and his built environment.
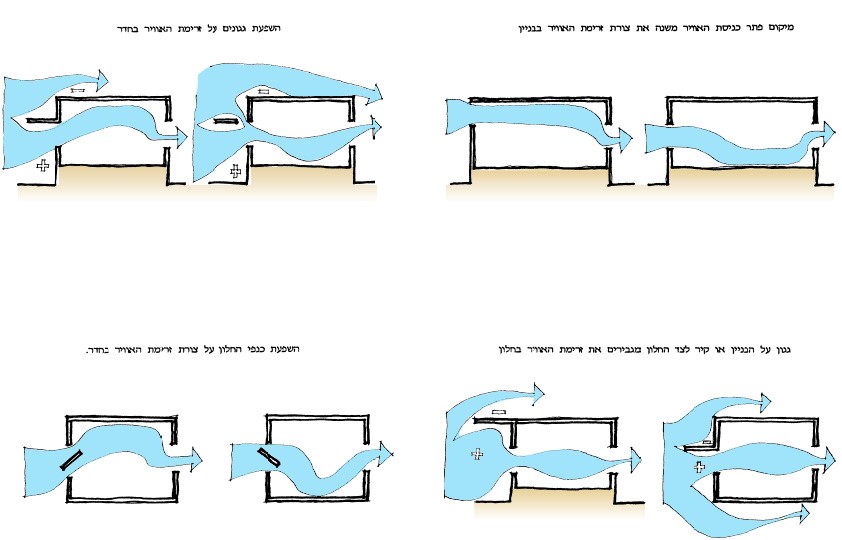
Common problems for all the desert areas are the winds, which carry with them dust and sand, the brightness and the dazzle.
The common factor in the frequency of the phenomena is the lack of cover for vegetation in the soil and the paucity of built-up areas.
Lack of awareness of the special environmental constraints of the desert may cause the design of buildings and structures that create conditions of poor comfort and thus an increased demand for energy to improve the microclimate.
Increasing awareness of environmental issues underscores the need for more efficient utilization of natural resources.
Desert architecture is an architecture that takes into account the characteristics of the desert environment, exploits its advantages and evades as much as possible the undesirable effects of its disadvantages.
Factors to consider planning:
Location of the plot:
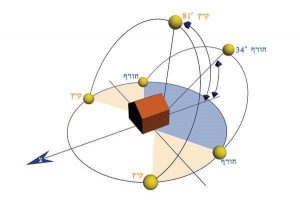
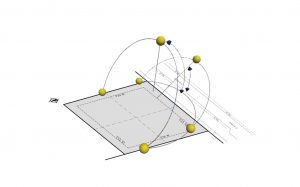
The location of the building on the lot is important to solve the range of factors affecting the amount of energy that will be received as a result of the building. The location of the various functions within the building in relation to the direction of the sun can also provide a solution for energy conservation.
|
The movement of the sun in the land of summer and winter Facades facing the sun according to season
Thermal insulation:
The most important factor for planning – is the building envelope.
Thermal isolation is crucial in terms of energy flow from within
Out and vice versa.
Thermal insulation reduces the inward flow of unwanted heat
During the summer, and reduces heat loss during the winter, so there is
It is very important to place the thermal insulation on the inside of The building envelope and not the exterior.
Shell color:
The exterior color of the building shell is a very important factor in its energy balance, surface temperature
The exterior of the building envelope will rise above the ambient temperature as it absorbs more solar radiation.

Size of openings:
The size and location of glazed openings is important Crucial in achieving thermal comfort in the building.
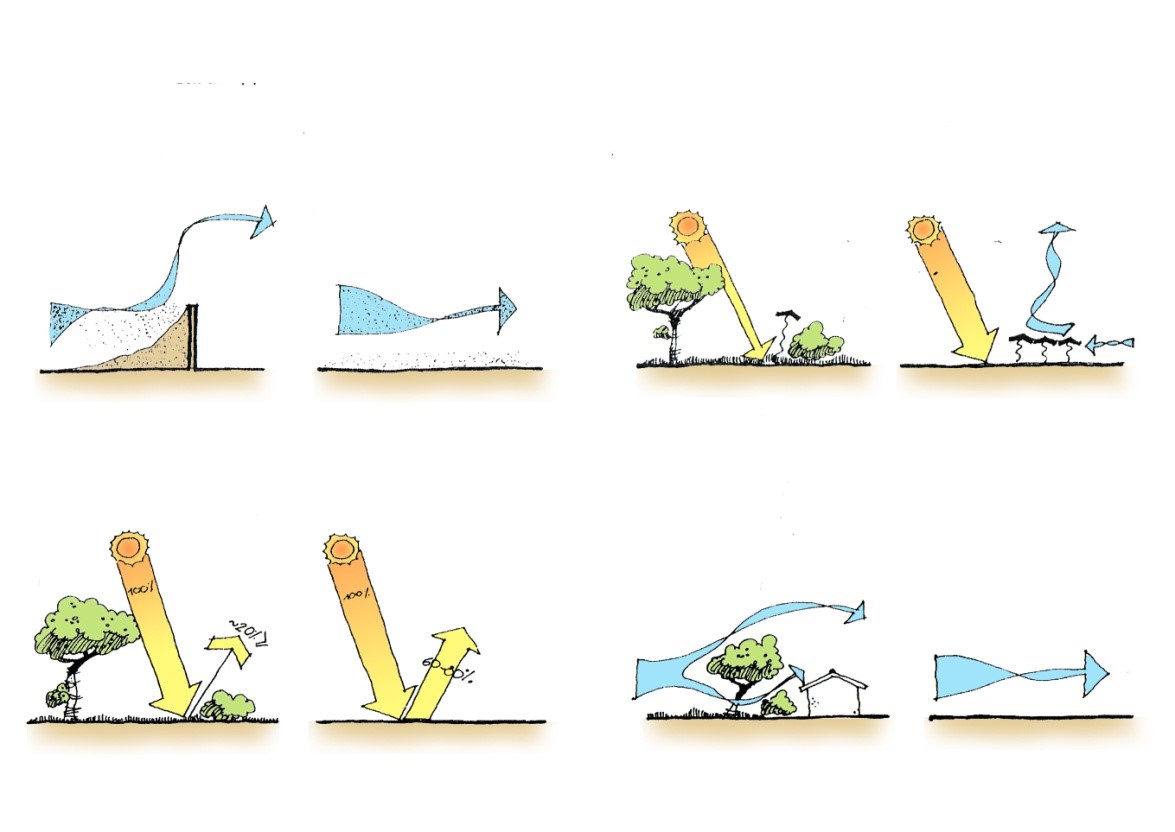
shadowing:
The data of solar radiation in the summer show that the penetration of solar energy
Unwanted through the windows of the building, causing increased load
Cooling significantly.
Air penetration:
Another important factor in the building’s energy balance is the air that enters it.
A certain amount of fresh air is needed for health reasons, but too much penetration can cause heat loss or overheating